7.0 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
7.5 SHALLOW DATA
Addressed was the communication of meaning though various transformations of information, either between agents of similar domains or agents of different domains. Information transformations throughout a system can be characterized in terms of layers of information or levels of abstraction or synthesis. There is a tendency for information to become hidden beneath such multiple derivations, abstractions, and mappings of data.
This research settled on a declarative approach as best for flexible evaluation. This approach necessitates a flattening of information within the sign instantiation so that there need be no other levels of information to explore beyond that of the icon and object. From the same perspective, the flattening model allows each instantiation to be accessed at the same level, so that there need be no other levels of information beyond that of the instantiation.
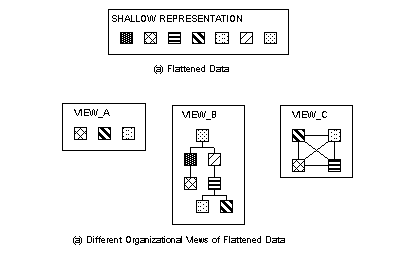
Figure 84 depicts a shallow data representation and possible views imposed upon this structure. To accommodate multiple views there exists a shallow, underlying stratum within which all data equally resides. An egalitarian approach such as this provides equal access and an open ended set of object to which a variety of views, including the traditional hierarchy can be imposed. Although not shown here, the view models should themselves part of the object set to allow for self-referentiality.
Having such a set of independent objects, exploration can of the shallow representation can be declarative rather than procedural, This allows the user to specify what is to be accomplished rather than how to accomplish it.
Figure 84 Reconstruction of Modeling Elements